Structural Variation Detection
NextGENeLR provides fast and accurate alignments of long sequencing reads and enables accurate detection of structural variants.
NextGENeLR uses a specialized long read alignment algorithm. This alignment algorithm works by first indexing the reference sequence, compressing homopolymer regions, which allows homopolymer length differences to be tolerated during alignment. A separate index table is saved for each chromosome. Reads are also similarly indexed. Each chromosome table is then searched for matches. The region with the most and longest matches is selected and a local alignment is performed. The long reads can be split to properly align reads containing structural variants. For each read the alignment positions for each section are compared to the reference. Any differences between the reads and reference are evaluated to determine the structural variant type, as shown in Figure 1 below. If sections of a read align to different chromosomes than a translocation is reported. If sections of a read align in different directions, then an inversion is reported. Similar breakpoints, within 5bp, are merged.
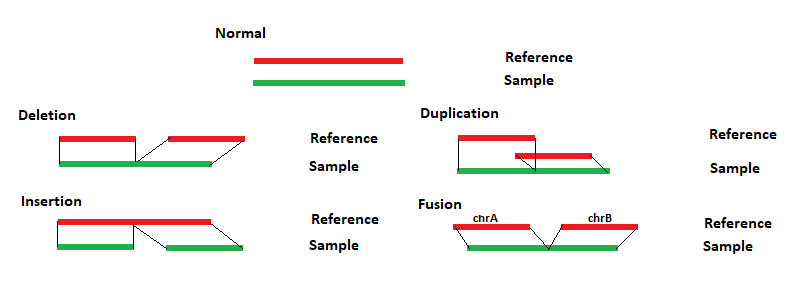
Figure 1: NextGENeLR makes structural variant calls by comparing the alignment positions for the sample and the reference. The patterns above illustrate how the structural variant type is reported.
Once analysis is completed the generated BAM file can be viewed using NextGENeLR’s Alignment Viewer. The Structural Variation Table is shown by default, with the Pileup Viewer above the table.
The Structural Variation Table lists the detected structural variants. For each variant, a type is provided as well as the number of reads supporting the structural variant, the breakpoint positions, the frequency of the variant out of the total reads aligned at each breakpoint position, and the distance in bp for the sample and the reference.
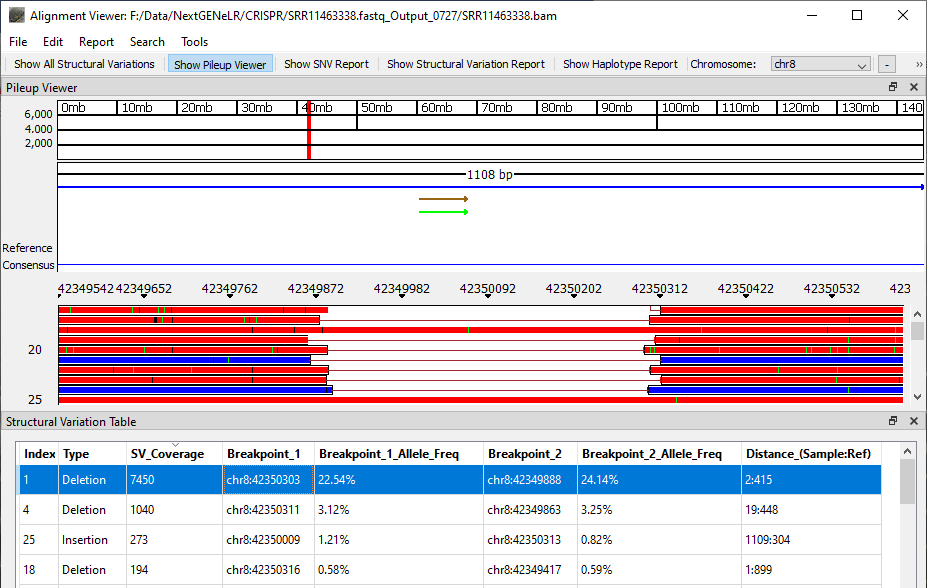
Figure 2: NextGENeLR Alignment Viewer showing the Structural Variation Table. Highlighted is a 413bp deletion.
Application Notes:
Trademarks property of their respective owner













