

Somatic mutation analysis of NGS reads from Illumina® iSeq, Miniseq, MiSeq, NextSeq, HiSeq, and NovaSeq systems, Ion Torrent Ion GeneStudio S5, PGM, and Proton systems as well as other platforms presents a significant challenge as these variants are often found at low frequencies, many times as low as 1%. Lowering variant calling thresholds to detect these variants in lower coverage exome analyses often result in the increased reporting of false positives due to chemistry and sequencing errors. Additionally, it is necessary to differentiate the somatic mutations from non-somatic variants that are also present in the sample.
A Somatic Mutation Comparison Tool is available in the NextGENe Viewer Comparison menu, which in testing has reduced false positives by 70%.
This specialized version of NextGENe software's Variant Comparison Tool allows the user to load three projects- a tumor project, a matched normal project (such as a blood sample), and a pooled project consisting of multiple normal samples.
The tumor and normal projects are used to find somatic variants by filtering out variants that are shared in both projects. The pooled project, ideal for lower coverage exome analyses, is used to eliminate artifacts due to library preparation and alignment by filtering out variants that occur in both the tumor and pooled project.
When the coverage from the liquid biopsy samples are around 10000x, as in the case of targeted PCR, the somatic comparison can be performed using only the tumor sample and normal control – no pooled project. In this case it is vital that the chemistry used to amplify the circulating tumor DNA produces reads that are directionally balanced in order to minimize false positives.
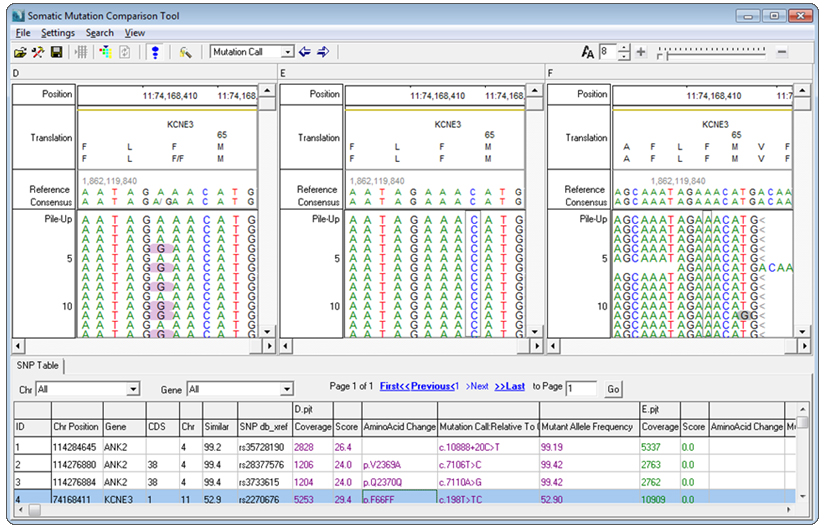
Figure 1: Somatic Mutation Comparison Tool with tumor, normal, and pooled normal projects loaded
In tests using 5 pooled normal samples the number of false positive calls has shown a reduction of up to 70%. Many of the remaining false positives were caused by common variants and systematic errors that appear in the tumor sample but were not called in the control sample due to low coverage. Increasing the coverage of the pooled normal samples will reduce the artifacts and maintain the specificity to the somatic mutation allele.
Application Notes:
Webinars:
Pricing & Trial Version:
Reference Material:
Trademarks property of their respective owner